Parasites in biology are considered to be organisms that carry out their vital activities at the expense of organisms of other biological species.
The important activity of these parasites is not beneficial to the host organism and, at the very least, such interactions do not lead to the development of negative effects.
Worst of all, parasites cause host death. In this case, either the parasite fled to the external environment, or joint death.
Human parasitic diseases have been practically known since the primitive era of human existence. This fact is evidenced in the process of observing the behavior of human ancestors - apes. Parasites that inhabit feathers are detected by monkeys and kept away from each other. This process has a very important social interaction character.
Human intolerance to the appearance of acne and pores on the skin also originated from the early era of human existence. Some insect parasites in the tropics can lay their larvae on the skin. This leads to a reflex urge to remove it from the skin.
Various helminths affecting the eyes, skin and gastrointestinal tract are described by ancient scientists. In the 18th-19th centuries, with the expansion and introduction of microscopy into medical practice, scientists proved the cause and mode of transmission of parasites that can cause certain diseases in humans.
- The beginning of the 20th century and the discovery of antiparasitic agents allowed humans to overcome most parasitic diseases.
Thus, mankind has been side by side with various parasites throughout its history. However, modern medical science makes it possible to diagnose the entire spectrum of parasites quickly and accurately, giving physicians the opportunity to treat the disease in the shortest possible time and with minimal risk for patients.
General practitioners will help identify parasites in the human body, their symptoms and treatment. Sometimes infectious disease specialists with a narrower specialization - parasites - can get involved for this.
What is a parasitic disease?
Parasitic disease is a nosology that arises after the introduction (invasion) of biological agents into the body. The latter is called a group of human parasites. The symptomatology of such a disease varies greatly and depends precisely on the agent that has taken root and carries out its life activities in the body.
According to the way parasites affect the human body, they are usually divided into the following groups:
- Exoparasites that affect human skin and hair.
- Toxic effects of parasitic waste products on the body.
- Damage to the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract and lungs by parasites.
- Formation of cysts and cysts in human organs. Increased cyst size and such cysts lead to specific symptoms of organ compression.
- Normal food channel disorders through the gastrointestinal tract. This can lead to intestinal intussusception (more common in children) or the development of intestinal obstruction.
- Parasites that live in a person can cause sensitivity and nonspecific allergic reactions.
- Microparasites can interfere with blood cell function, causing fever and intoxication.
- The effects of some types of parasites on the body not only lead to severe symptoms, but can also lead to organ failure or death.
Various negative effects of parasites that arise in the body are due to different biological species that are incorporated into human organs. However, the biological diversity of parasites living in the human body allows doctors to identify the symptoms of certain parasitic diseases.
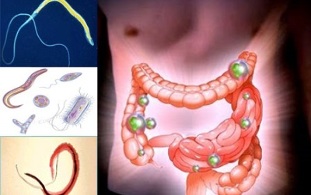
Parasites that live in the human body
The main means of human infection with parasites depends on the life cycle of biological organisms, which are the causative agents of parasitic diseases.
Doctors identify parasitic ways to penetrate a person such as:
- Contact path.This is a characteristic of exoparasitic insects, as well as some helminths that live mainly in water, larvae that attack under human skin. You can be infected this way both from sick people and through linen, bedding, contaminated personal or public hygiene items, and so on.
- Fecal-oral routeinfection. Occurs when pathogenic cysts enter food after contact with infected feces, especially from animals. Autoinvasion can also be observed - infection of a person if personal hygiene is not observed, and so on.
- Pollution.Pathogens enter the bloodstream when infected insects are destroyed.
- Infectious infections.Parasites enter the bloodstream when bitten by insects that carry the disease. Often, these contagious pathways are specifically for the simplest parasites, for example, malaria.
- Sexually transmitted infections.This is typical for sexually transmitted diseases caused by parasites and for some helminths that can affect a person's urinary and genital tract.
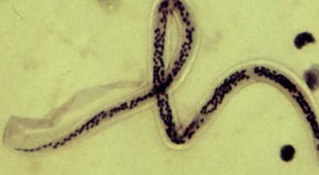
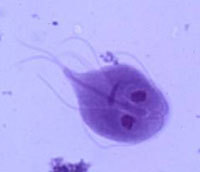
Protozoa, helminths (round and flatworm), insects, and even some types of fungi caused by parasitic diseases
The occurrence of humans with this species depends on geographical and climatic zones. Therefore, each country medicine keeps its own record and a list of parasites specific to it.
Biological organisms that enter the human body have been studied in detail by medical biologists and doctors, which makes it possible to clearly classify all biological species that can cause parasitic diseases: Chagas disease, leishmaniasis, malaria, giardiasis, trypanosomiasis, toxoplasmosis, trichomoniasis).
Signs of parasites in the human body

Unfortunately, there are no exact signs of parasites in the human body and there are no symptoms that indicate this or that type of parasitic infection. This leads to the fact that for an accurate diagnosis, for example, helminthiasis, special tests are required.
In contrast, almost all exo infections are moderately diagnosed - based on the clinical picture and the presence of certain types of insects on the skin.
In general, all symptoms of parasitic diseases can be grouped into the following groups:
- Itching and skin discomfort caused by parasites of hair and external skin (lice, lice, etc. ). Skin rashes such as acne and itching are often associated with conditions such as demodectic mange (a special type of lice).
- Pain in various parts of the body due to the entry of parasites into the skin and muscles (some types of worms that live in water).
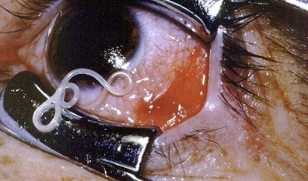
- Pain in the eyes, blurred vision.
- Pain in the lungs, coughing phlegm (this condition can occur specifically for the migration of ascaris larvae in the lungs, as well as echinococcal cysts of the lungs, etc. ).
- Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea are very common symptoms in most helminths that are parasitic of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Jaundice, disorders of the liver and bile ducts, liver failure. These symptoms occur with helminths affecting the liver and bile ducts, as well as with malaria at the peak of the disease.
- Stomach ache.
- Intestinal obstruction due to closure of the intestinal lumen by a large number of ringworms or large representatives of flatworms.
All symptoms of the presence of parasites in the human body, if there are no data for other pathologies, should encourage doctors to think of parasitic human disease and serve as the basis for diagnostic and laboratory studies.
Diagnostic parasites in humans
Depending on the type of parasite that has invaded the human body, one or one study was conducted. If we talk about external exoparasites, which are mainly insects, then the diagnosis of the disease is usually limited to general examination, as well as microscopy of insects.
A general examination usually provides an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment or cleansing of the scalp or skin. In the case of demodicosis or scabies, a diagnosis can be made easily based on the location of the rash and the presence of itching.
Fractions taken for microscopy in this case confirm the diagnosis of intradermal parasites.
For gastrointestinal parasites, a primary screening study (a diagnostic procedure that allows you to quickly and relatively assess information about the presence or absence of disease in a large number of people) is a stool analysis.
- With a special stool microscopic examination, the laboratory assistant assesses the presence of worm eggs, dead worms, cyst capsules and so on.
With the morphology of helminth eggs, you can almost pinpoint the type of parasitic worm in the body. Sometimes in the stool, the tapeworm portion is determined macroscopically. They were then examined under a microscope to determine the appearance of flatworm parasites in the gastrointestinal tract.
In some cases, for example, when the diagnosis of parasites in the body is not possible by analyzing feces or informative, immunological studies are used. They allow you to assess the presence of antibodies to specific types of helminths. Unfortunately, due to the special immunological relationship between the human immune system and parasites, antibody levels in some cases may not reflect the true picture of the disease.
In the case of malaria, a drop of thick blood is tested to detect Plasmodium malaria. Also, general blood counts, leukocyte levels, as well as all blood biochemical parameters, especially liver, were assessed.
The presence of increased blood eosinophil levels is a frequent sign of not only allergic diseases, but also helminthic invasion. This is the first "bell".
Sometimes helminths in the gastrointestinal tract are diagnostic findings during contrast radiography, cystoscopy, FGDS, colonoscopy.
How to get rid of parasites in the human body?
Treatment of parasitic infections can only be done by a doctor, subject to certain rules.
Self-medication and traditional medicine in such cases do not bring improvement, and can sometimes be fatal.
It is also important to provide preventive treatment for all family members and acquaintances.
Human exoparasites, which carry parasites on hairy parts of the body, are destroyed with a special disinfectant. Usually, one treatment is followed by cleansing enough to kill exoparasites.
When it comes to skin parasites (scabies, fever blisters), special ointments containing pesticides on the organism are used.
Antihelminthics are used against round and bloated worms, which act on the main lumen of the gastrointestinal tract especially on helminths. Depending on the biological type of helminth, various treatment regimens are used (from one tablet to a series of courses).
Such drugs should be used strictly under the supervision of a doctor in order to recognize the effects and side effects of the drug in a timely manner.
There are no other treatment methods, detoxification programs, etc. that can cause the death of parasites in the body completely and, as a consequence, for the healing of a person.



























